
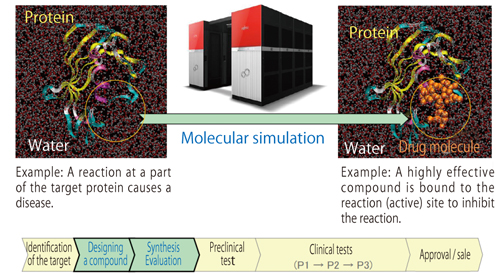
Fig. 1:Fujitsu developed OPMF, a software for designing a low-molecular weight compound which strongly binds to and inactivates the target protein which causes a disease, enabling highly effective novel compounds to be created in a short period of time at low cost.
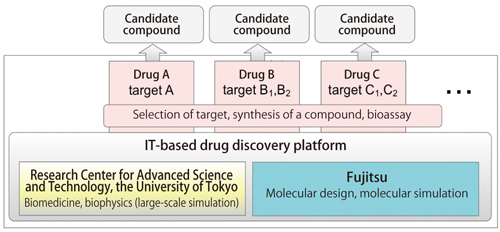
Fig. 2:Schematic view of joint studies on IT-based drug discovery between Fujitsu and RCAST and pharmaceutical companies.
The IT-based drug discovery by Fujitsu
━Why is Fujitsu working on the R&D of IT-based drug discovery ?
Kamiya Fujitsu started to import and sell computational chemistry software and develop original software programs jointly with research institutes and companies in Japan in 1983, which is more than 30 years ago. At the time, Japan was behind the USA, etc., on software development. For example, let’s say that a university bought a supercomputer, but they could not use it effectively. So we started in-house software development full-scale. In 2003, the sequencing of the human genome was completed, providing an impetus to the biotechnology industry. Fujitsu established the BioIT Business Development Unit (present Next-Generation Healthcare Innovation Center) in 2004 to accelerate the bio-related business, and has also concentrated its efforts on technologies called IT-based drug discovery, which use computational science, through its own research activities and collaboration with companies, universities and research institutes in Japan and overseas.
━What is the IT-based drug discovery targeted by Fujitsu?
Mitsui Conventional drug discovery involves the selection of possibly promising candidates for drugs among a vast number of low-molecular weight compounds by using the experience and knowledge of researchers, and repeating synthesis and experiments. According to one’s estimate, out of a total number of candidate compounds, only one out of thirty thousand is finally approved as a new drug. The process requires a long time, may be a decade or longer, and costs several tens of billions of yen. Our drug development technology involves using computer simulation to design the structure of a compound, virtually on the computer, that has drug efficacy based on the structure of the target protein, and creating a new compound in a short period of time at a low cost. We also have developed technologies for predicting and evaluating the activities of drug candidates by molecular dynamics simulation that assumes a biological environment.
Kamiya The technology is characterized by the capability of designing diverse chemical structures, which may not be found in existing compounds, and narrowing them down to promising ones before synthesis and evaluation. For this purpose, Fujitsu developed original software for designing low-molecular weight compounds, which is called OPMF (Optimum Packing of Molecular Fragments). Based on the three-dimensional X-ray structural analysis of the (target) protein, a new compound that can bind to the active site is designed by connecting fragments. The efficacy of the chemical structure so obtained is then predicated by using MAPLE CAFEE for an environment that reproduces biological conditions, including the water molecules surrounding the protein.
━Is MAPLE CAFEE different from MP-CAFEE?
Kamiya When Prof. Fujitani was in Fujitsu Laboratories, he constructed a force field that uniformly processes biopolymers such as proteins and organic molecules, and developed a method for calculating the molecular dynamics from the state in which the protein and compound are separate until they are bound, and determining the binding free energy. This calculation method is called MP-CAFEE. MAPLE CAFEE is the name of the system constructed by Fujitsu by using this calculation method.
Construction of IT-based drug discovery platform jointly with RCAST
━You started joint studies with RCAST in 2011.
Mitsui During the process of doing R&D toward the creation of low-molecular weight drugs by using computer simulation, RCAST appreciated the technologies of Fujitsu for designing and evaluating low-molecular weight drugs; and we started joint studies. In concrete terms, Fujitsu designs low-molecular weight drug candidates by using OPMF, narrows them down to likely promising ones, and provides the information to Fujitani Laboratory in RCAST. At the Fujitani Laboratory, they calculate the extent the compound acts on the protein via simulation. They notify the results of the analysis to Fujitsu, and Fujitsu feeds back the data into the design. Through this joint study, we are also using the computational power of the K computer, although indirectly.
Kamiya For the Theme 2 in FY 2012, Fujitsu designed about 300 compounds for a target protein in cancer therapy, and the binding free energy was calculated using the K computer. Last fiscal year, the results were used to improve studies and further elaborate the designs of the compounds. We chose 25 compounds from them, and calculated their binding free energy. Eight compounds were predicted to have strong binding free energy, and studies will start jointly with the experimental group toward development of drugs for a cancer remedy.
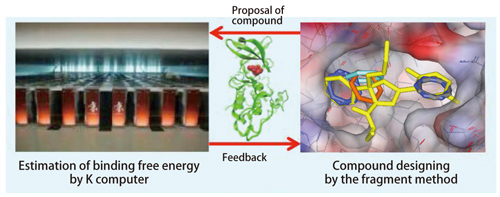
Fig. 3:Schematic view of the joint study between Fujitsu and RCAST on Theme 2. Fujitsu designs candidate compounds, and the results of binding free energy calculation are fed back and used to elaborate the design.
━What is the goal of Fujitsu in the joint study with RCAST?
Mitsui We aim to construct a platform for IT-based drug discovery, which innovates the development process, by using the excellent study knowhow and results of RCAST, the large-scale simulation technology performed by Prof. Fujitani et al., and the molecular design and simulation technologies of Fujitsu. We will also conduct joint studies with a pharmaceutical company to produce the fruits of new drugs by IT-based drug discovery.
━What are the current issues in R&D?
Mitsui The biggest problem is the computational power. We want to quickly check how the efficacy changes by a change in the design of a compound, and reflect the results for improving the compound. In other words, we want fast cycles. However, calculation of binding free energy requires a vast amount of computation, and thus we want to use as high a computational power as possible. It would be meaningless to use IT-based drug discovery if it is faster to actually synthesize the compound than calculating.
━What do you think about the future of IT-based drug discovery ?
Kamiya IT-based drug discovery is a highly promising new-generation process for developing innovative and highly effective compounds in a short period of time at low cost. We believe that establishment and application of this innovative technology will help to create new therapeutic drugs for various diseases. It would be wonderful if computational science can contribute to improving medicine, such as making it possible to cure diseases that are difficult today. We mentioned that the success rate of a new drug is one out of 30 thousand. This means that we need to synthesize thirty thousand compounds to develop one drug. If such experiments can be replaced by computation, it would sharply reduce the labor and difficulties for developing a drug. Also to achieve this goal, we want to produce results as early as possible.
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|---|











